Cytoneurin: what it is for, how to use it and side effects
Content:
Citoneurin is a medicine that contains in its composition B vitamins such as thiamine (vitamin B1), cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) and pyridoxine (vitamin B6), which exert an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, being indicated for the treatment of pain. or inflammation in the nerves in conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, fibromyalgia, or pain at the end of the spine, for example.
This medicine is sold only with a doctor's prescription and can be purchased in pharmacies or drugstores in the form of pills or injectable ampoule to be applied to the muscle, by a health professional such as a nurse or pharmacist.
Citoneurin may also contain dexamethasone in its composition, a type of steroid with strong anti-inflammatory action, being sold with a prescription, in the form of an injectable ampoule with the trade name Dexa Citoneurin.
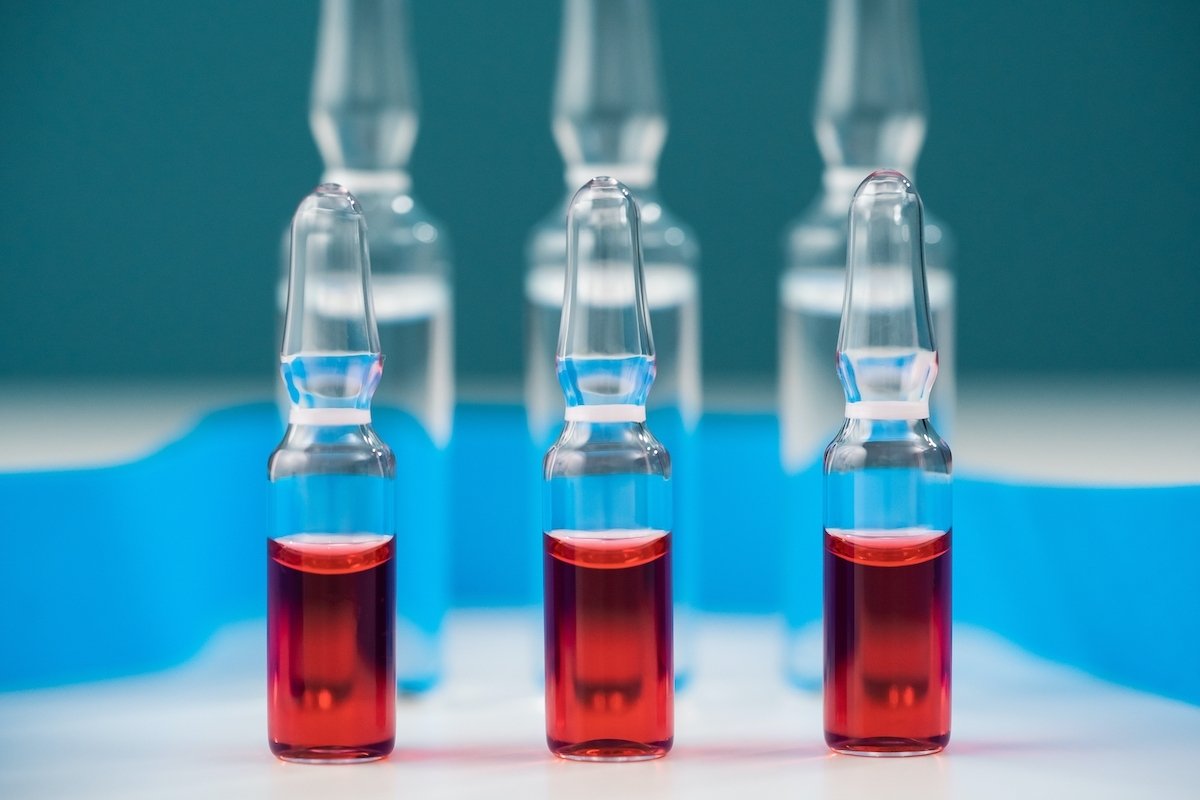
what is it for
Citoneurin is indicated for the treatment of pain or inflammation of the nerves, as it has analgesic and anti-inflammatory action, favoring the regeneration of nerve fibers.
The main indications for treatment with Cytoneurin include:
- Severe pain or inflammation in the nerves;
- Pain at the end of the spine;
- Fibromyalgia;
- Carpal tunnel syndrome;
- Inflammation of the nerve root;
- Diabetic neuropathy;
- Pain that starts in the neck and radiates to the arm.
In addition, Citoneurin can be indicated as a vitamin supplement for people with B-complex vitamins deficiency due to restrictive diets or after bariatric surgery, for example.
Citoneurin should always be indicated by the doctor evaluating health conditions individually.
How to use
Citoneurin should only be used by adults and the form of use varies by presentation and includes:
1. Injectable cytoneurin
Injectable Citoneurin should be used as directed by a general practitioner or orthopedist, for example, and applied to the gluteal muscle by a healthcare professional trained in injection administration, such as a nurse or pharmacist.
The dose of Cytoneurin may vary depending on the disease and includes:
- Nerve pain or inflammation: the recommended dose is 1 ampoule of Citoneurin 1000 or 5000, every 3 days;
- Vitamin supplementation: the recommended dose is 1 ampoule of Citoneurin 1000, once a day, or 1 ampoule of Citoneurin 5000, once a week.
Doses and treatment time may vary according to medical evaluation and guidance.
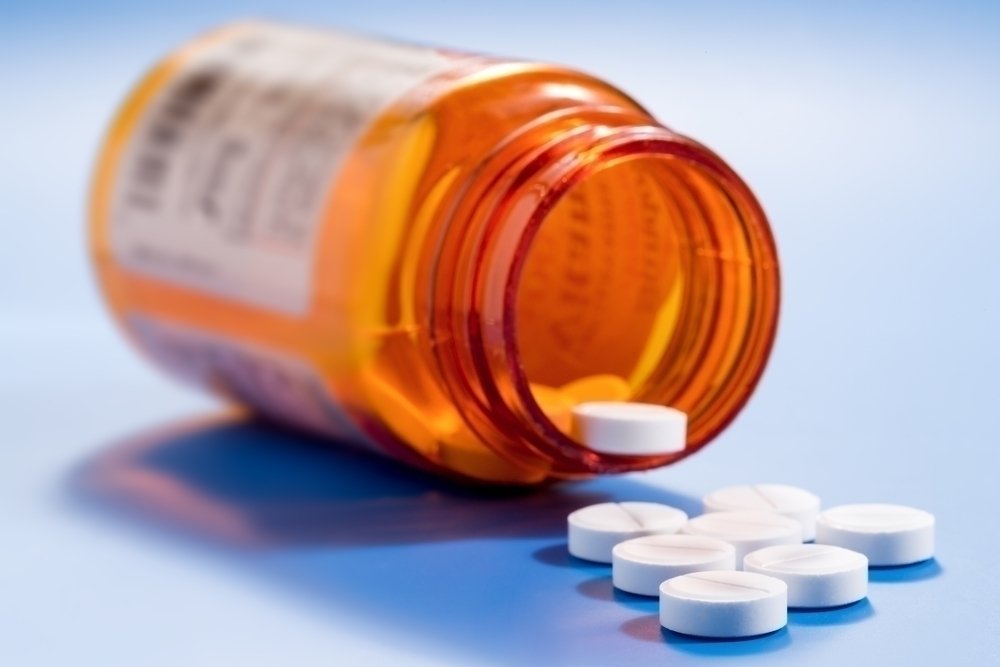
2. Cytoneurin tablet
Citoneurin tablet should be taken with a glass of water, after a meal. The tablet must be swallowed whole without breaking, without chewing, at the times established by the doctor.
However, in case you forget to take a dose at the right time, take it as soon as you remember, but if it is close to the time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and wait for the next time to take it. Do not double the dose to make up for the missed dose.
How Cytoneurin tablets are used varies depending on the disease and includes:
- Nerve pain or inflammation: the recommended dose is one tablet, 3 times a day, this dose may be increased by the doctor in more severe cases;
- Vitamin supplementation: the recommended dose is 1 tablet once a week.
The duration of treatment with Citoneurin tablet should always be done according to medical advice.
Possible side effects
Some of the side effects that may occur during treatment with Citoneurin are pain and irritation at the injection site, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, excessive sweating, rapid heartbeat, itching, hives or acne.
In addition, Injectable Cytoneurin can cause an allergy with symptoms that can start immediately after the injection, such as difficulty breathing, feeling of a closed throat, swelling in the mouth, tongue or face, general discomfort, feeling faint, redness or itching of the skin. . Therefore, injectable Citoneurin must be applied by a healthcare professional so that first aid can be provided immediately.
who shouldn't use
Citoneurin should not be used by children, pregnant or breastfeeding women, or people with Parkinson's disease who are taking levodopa.
In addition, Citoneurin should also not be used by people who are allergic to vitamin B1.
Leave a Reply
In order to leave comments, you need to log in



0 Comments